Knowledge
Thermal Expansion and Shrinkage of the Bushing

Thermal Expansion and Shrinkage of the Bushing
Basic introduction
When a material is heated, its molecular motion intensifies, causing the material to expand; As the material cools, the molecular motion weakens and the material shrinks. This size variation can affect the accuracy and functionality of the product.
The thermal expansion and contraction of plastic is obvious, about 4~10 times different than that of metal, the size change is directly proportional to the temperature change, the amount of change varies according to the material, depends on the expansion coefficient, the temperature rises, the size becomes larger; The temperature drops and the size decreases, so special attention needs to be paid to the application.
Cooperation and Combination Problems
In mechanical assembly, different materials have different expansion coefficients, which will lead to poor fit. For example, if the metal shaft and the plastic bushing expand or contract differently under temperature changes, it may cause the bushing to be too tight or too loose, affecting the operation of the machine.
- Loose lining: If the bushing and shaft expand due to increased temperature, they can become too loose, which can increase friction and lead to poor running or even damage.
- Overtight Bushings: Conversely, when the temperature drops, the material shrinks, and the bushings and shafts may become too tight, leading to increased vibrations and inaccurate positioning.
Solution
- Choose the right material: Choose materials with similar coefficients of thermal expansion to ensure they expand and contract similarly under temperature changes, reducing fit issues.
- Design reserved space: Consider temperature changes in the design of the fit, and give an appropriate margin so that it can still maintain a good fit during thermal expansion or contraction.
- Use Lubricants: Proper lubrication can reduce friction and wear, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Reasonable increase in interference: Interference allows the bushing to become dimensionally stable in the face of rising and falling environmental and working temperatures.
- Temperature control measures: maintain a stable temperature in the operating environment to avoid excessive temperature fluctuations, which can reduce the impact of thermal expansion on the fit.
- Maintain cooling: Continuous cooling can control the operating temperature of the bushing within a certain range, suppressing excessive temperature and avoiding changes in material strength, coefficient of friction and size.
Illustrated examples of bushings installed in holes or shafts, with various scenarios of bushings below, are helpful for how to design and improve the bushings under thermal expansion and contraction.
Because in order to facilitate readers’ understanding, it is presented in an exaggerated way, which cannot be seen directly with the naked eye, and requires measurement, observation of data and actual installation to see the problem, so it is for reference only.
Practical application example, when Thermal expansion
When the bushing is already installed on the shaft
When the Bushing is installed on the shaft, the thermally expanded lining will create a gap with the shaft, which will affect the drop of the pull-out force, or even fall off and increase in size. There will be abnormal vibration, loss, and poor operation when falling off.
- Improvement 1: The mounting method of the bushing has been changed to be installed in the hole, and the expansion direction of the bushing has become around the hole, which has a stronger force and makes it less likely to fall off.
- Improvement 2: The inner diameter and outer diameter of the bushing are reduced, so that the amount of interference increases, and although the installation force is increased, the gap with the shaft can be avoided.
- Improvement 3: Change the material and choose a material that is less affected by ambient temperature, that is, a material with a smaller expansion coefficient, in other words, a material with less change in size when the temperature rises, which can also be called dimensional stability-temperature.


The shaft liner is applied to the bore and is unidirectionally suppressed
When the height of the thermal expansion of the bushing changes, it becomes higher than before, and if the depth of the hole is exactly equal to the height of the bushing, the bushing will be exposed and protruding.
- Improvement 1: Reserve the space for expansion and increase the depth of the hole (extend the height of the hole).
- Improvement 2: Changed the design.
The liner is applied to the hole and is bidirectionally suppressed
The shaft lining is applied to the hole, and the height of the bushing should be higher due to thermal expansion, but it is limited and presented in a twisted and deformed way, resulting in a small inner diameter size. On the other hand, if the bushing is installed on the shaft and is in bidirectional suppression, thermal expansion will cause the bushing to twist and deform, resulting in a larger outer diameter size.
- Improvement 1: Leave room for expansion.
- Improvement 2: Changed the design.


When assembling the shaft liner in the hole
Thermal expansion will increase in size, making it difficult to install or increase the compression force.
- Improvement 1 : How to reduce the compression force?[link]
Practical application example, when cold shrinkage
The shaft liner is applied to the hole
Cold shrinkage will affect the drop in pull-out force, or even fall off, and the outer diameter size becomes smaller. There will be abnormal vibration, loss, and poor operation when falling off.
- Improvement 1: The mounting method of the bushing has been changed to mount on the shaft
- Improvement 2: The inner and outer diameters of the bushing are increased, and the interference is increased.
- Improvement 3: Changed the material to make it less affected by ambient temperature. (Dimensional Stability – Temperature)

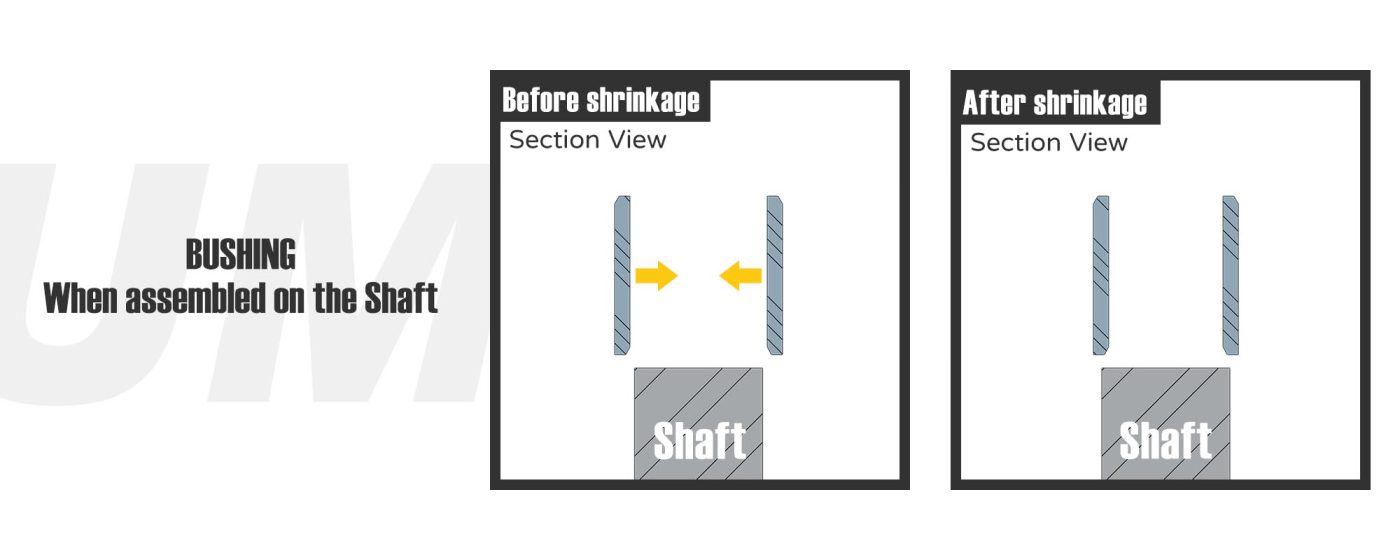
When the shaft lining is assembled on the shaft
Cold shrinkage will reduce the size, resulting in poor installation or high compression force.
- Improvement 1 : How to reduce the compression force?[link]

It will be considered that thermal expansion and contraction mainly include the following situations:
- The foreign environment is a high-temperature area.
- The foreign environment is a cold region.
- The temperature rises when it runs continuously for a long time.
- High speed and high load design.
- Precise dimensions are required.
Plastic expansion coefficient
| Material | Expansion coefficient Unit: / °C |
|---|---|
| Polyoxymethylene, POM | 0.000085 |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE | 0.000145 |
| Polyetheretherketone, PEEK | 0.000050 |
| Nylon 46 | 0.000080 |
| Nylon 6 | 0.000080 |
| Nylon 66 | 0.000072 |
| PEI | 0.000055 |
| Material | Expansion coefficient Unit: / °C |
|---|---|
| PI | 0.000110 |
| PPS | 0.000053 |
| PP | 0.000120 |
| PC | 0.000065 |
| PS | 0.000080 |
| PVC | 0.000050 |
| HDPE | 0.000120 |
The values of these expansion coefficients will vary depending on the specific formulation of the material and the conditions under which it will be used. If you have a specific purpose of plastic materials or more detailed needs, you need to consult the technical data or relevant literature of the material.



