Knowledge
What is the Thermal Expansion Coefficient?

What is the expansion coefficient?
Most objects and materials have a characteristic, the temperature rises, the size increases; The temperature drops, the size becomes smaller, the so-called thermal expansion and contraction, the object expands and contracts when it is heated, and contracts when it is cold.
A few materials are non-thermal expansion and contraction, as follows:
- Bronze is a rare material with the property of shrinking when heated and expanding when cooled;
- 0 to 4℃ water, water shrinks and expands within a specific temperature range;
- Quartz glass, with a coefficient of linear expansion of almost zero, is widely used in high-precision optical instruments and laboratory equipment, suitable for use in high-temperature environments.
- Ceramics, certain high-performance ceramics, such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and zirconia (ZrO2), have low expansion properties at high temperatures and are often used in electronic components and refractories.
- Fiber-reinforced composites, some use fiber reinforcement, such as carbon fiber composites, which have low thermal expansion properties and are commonly found in aerospace and sports equipment, providing high strength and stability.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
The expansion coefficient determines how much and less the size of the material expands and contracts. The higher the value, the greater the size change due to temperature; The smaller the value, the smaller the size change due to temperature changes. It is essential for design and analysis in engineering and scientific applications. There are several common types of expansion coefficients:
- Each unit of temperature change and length change is called the linear expansion coefficient, which describes the thermal expansion characteristics of the material in one direction. The metric unit is mm/mm °C [more commonly used]
- Each unit of temperature change and area change is called the surface expansion coefficient, which describes the thermal expansion characteristics of the material in two directions (i.e., area). The metric unit is mm2/mm2 °C
- Each unit of temperature change and volume change is called the volume expansion coefficient, which describes the thermal expansion characteristics of the material in three directions (i.e., volume). The metric unit is mm3/mm3 °C

Please refer to the plastic expansion coefficient of each material.
https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/linear-expansion-coefficients-d_95.html

Data
Different materials (substances) have different expansion coefficients. When the material is a single substance, it is recommended to directly query existing data instead of calculating the expansion coefficient yourself and looking for ready-made data.
It is more special for composite materials (referring to the mixture of two or more substances). When it is difficult to query, you need to implement and calculate the expansion coefficient yourself. Sometimes knowing the mixing ratio of the materials may be able to deduce the theoretical value. In addition, if it is an unknown material, you can roughly infer or filter out what kind of material it may belong to by calculating the expansion coefficient.
Reminder, when looking for information, pay special attention to °C and °F units, and convert them yourself.
What are the benefits?
Understanding the expansion coefficient is very important in engineering design to help improve product accuracy, reduce manufacturing waste, reduce assembly difficulty, and improve product life.

For example:
This is most evident when seasonal temperature changes, especially when some products are assembled for metal and plastic, cause part errors. In winter, the assembly is smooth, but in summer, the hole position runs away and is not aligned, and the engineer will correct it once if he does not understand the expansion coefficient.
When winter comes, it is found that the hole position runs back and is not aligned, so that it repeatedly causes a waste of cost, if the expansion coefficient is considered in the first product development, there is no need to spend so much energy, time and money, so some companies use all-weather air conditioning to reduce the problem caused by the material expansion coefficient.
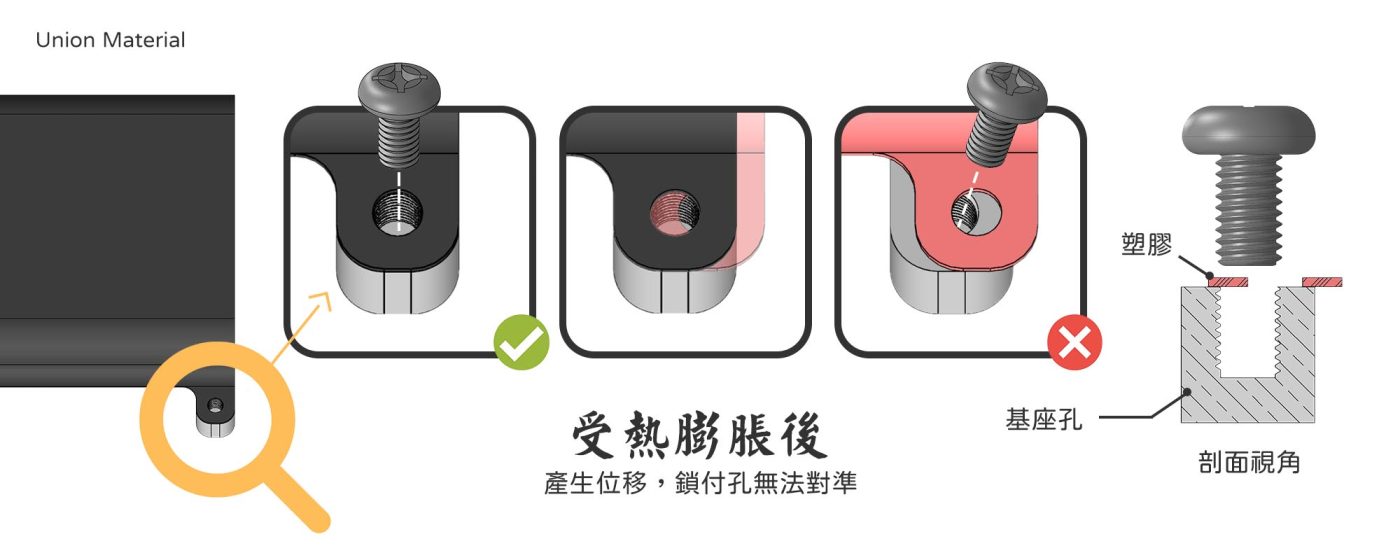
How to fix it?
- Change Design
- Change the material, the material that is less affected by the ambient temperature. (Dimensional Stability – Temperature)
- Reserve the size space that can heat up and cool
In addition, some stores must use air conditioning to maintain a certain temperature to avoid errors in size due to thermal expansion and contraction.
Examples of various industries:
The coefficient of expansion is widely used in a variety of industries, as many engineering and manufacturing processes must consider the behavior of materials under temperature changes. Here are some specific examples
- Construction engineering: Expansion joints are designed at both ends of the bridge to cope with the expansion and contraction of the bridge deck caused by temperature changes, and the expansion and contraction of building materials in different seasons should be considered.
- Mechanical design: cylinder and piston to ensure that the gap between various parts is maintained appropriately when the engine runs at high temperature, and the material with the expansion coefficient needs to be selected.
- Electronic components: PCB design ensures that electronic devices are not damaged due to thermal expansion during operation to avoid solder joint cracking and circuit damage.
- Bearings and linings: In high-temperature operating machinery and equipment, bearings and bushings with low expansion coefficient are selected to ensure stable operation of the equipment.
Other causes of expansion
In addition to the fact that substances change size (expansion) due to temperature increases and decreases, another reason is that the substance absorbs and loses water. The more moisture it absorbs, the larger the size; Conversely, the more water is lost, the smaller the size. For example: plastic nylon.
The expansion coefficient of each material
The following are the linear expansion coefficients of some common materials, which may vary over different temperature ranges, and are based on standard reference data.
| Substance | Expansion coefficient (/°C) |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | 0.000023 |
| Copper | 0.000016 |
| Iron | 0.000012 |
| Carbon Steel | 0.000007 |
| Glass | 0.000008 |
| Graphite | 0.000002 |
| Titanium | 0.000011 |
| Stainless Steel | 0.000015 |
| Tin | 0.000022 |
| Nylon | 0.000080 |
| Teflon | 0.000145 |
| Plastic steel | 0.000085 |
These values represent the amount of change per unit length of a material with each degree Celsius increase in temperature. For example, the linear expansion coefficient of aluminum is 23×10⁻⁶/°C, which means that for every 1°C increase, a 1-meter-long aluminum bar will increase by 23 μm.
Thermal expansion and contraction dimensions – Calculation Online
Thermal expansion and contraction dimensions, we provide calculation of the dimensional changes of each material after thermal expansion and cold contraction. If no material is found, select a similar material.



