Knowledge
What is Bearing
What is Bearing?

Noun Explanation
Bearing literally means bearing axis, a verb which can be imagined as to bear
As a mechanical part, it supports another axis (part) and provides a smooth and low-friction effect when performing linear and rotational motion.
Simply put, the shaft bears or carries the load. This is the bearing.

Bearings are small yet essential components found everywhere in industrial production and daily life. From car engines to power tools and household appliances, these often-overlooked parts play a crucial role. This article dives into the fascinating world of bearings, uncovering how these tiny components are indispensable in modern technology and highlighting the intricate design behind them.
Function of bearings
Bearings primarily serve to minimize friction, support rotational motion, and enhance the smoothness and efficiency of mechanical devices.
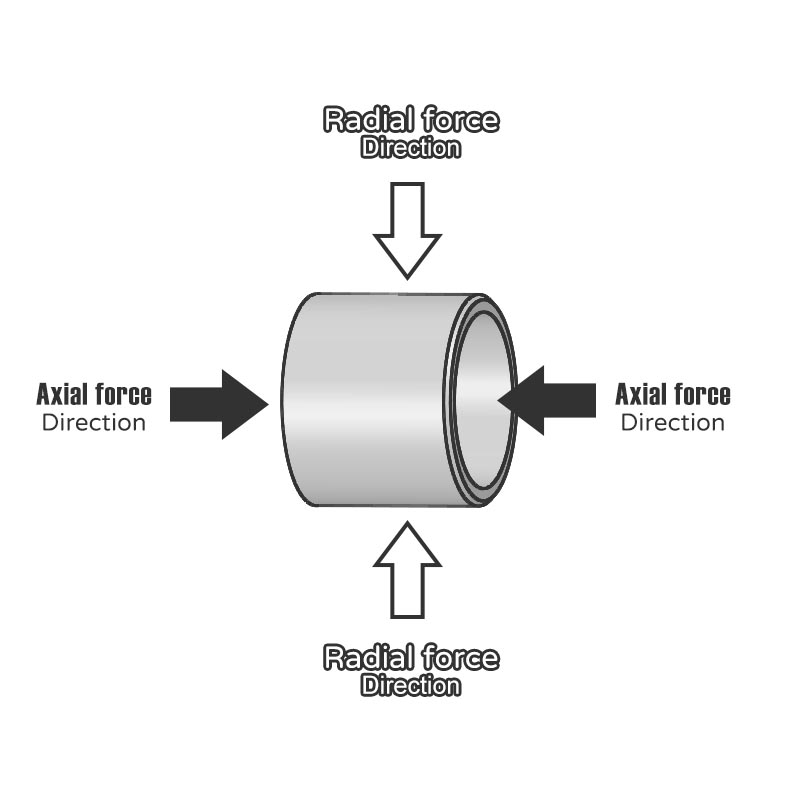
Application and Force
Bearings are essential for enabling rotational and reciprocating linear motion in shafts. During use, they must handle forces from various directions, including radial and axial forces.
Radial force: refers to the force perpendicular to the bearing axis. For example, it usually comes from gravity, self-weight, belt tension, etc.
Axial force: refers to the force that acts parallel to the bearing axis, typically resulting from thrust or pressure applied along the axial direction. For instance, in certain situations, when a bearing is installed alone, a significant axial force may be necessary.
Combined force: Most of the time, bearings need to bear radial force and axial force at the same time. For example, in some cases, the radial force is greater than the axial force, which is typical for drive shafts, transmission shafts, and rollers. It is relatively rare for the axial force to be greater than the radial force, which is typical for screws and pumps.
In essence, bearings are crucial for minimizing friction and supporting rotational motion in mechanical systems. By carefully understanding, designing, and selecting the right bearing specifications, types, and materials, you can achieve efficient performance, long-term durability, and cost savings for mechanical equipment.
Used in industries
Automobiles, bicycles, electric vehicles, general engineering, heavy industry, aviation, railways, etc. For example:
Automotive Industry: bearings are essential components used throughout automobile manufacturing. From engines and gearboxes to wheels and steering systems, nearly every moving part depends on bearings to function. High-performance ceramic bearings are particularly important in racing cars, enhancing both speed and durability.
Aerospace: Bearings are equally important in the aerospace field, where they are used in helicopter propellers, aircraft engines, landing gear, flight control systems, etc. These bearings must be able to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures and maintain high reliability.
Home applications: Electric tools, washing machines, fans and other electrical appliances we use every day rely on bearings to keep running smoothly. Even the doors, windows and drawers in the home often have bearings hidden inside.

Type
There are many different types of bearings, each designed to meet specific application requirements. The following are common types of bearings:
- Ball Bearings
- Needle Roller Bearings
- Sliding Bearings
- Oil-retaining Bearings
- Self-aligning Bearings
- Thrust Bearing
- Pillow Block bearing
- Linear Bearings
- Self-lubricating bearings (UnionMaterial belongs to this category)
With so many types and functions, it’s impossible to cover each one in detail. Selecting the right type based on its application ensures optimal performance, stability, and durability of mechanical equipment parts. Ball bearings are among the most common types, primarily used to handle radial loads and light axial loads. Their design consists of four key components: the inner ring, outer ring, retainer, and ball, all working together to minimize friction and wear.
What the Local Industry says
Bearing is a general term, often referred to as Pei Lin in the local industry, which is a transliteration of the English word “bearing”. Today, many different subcategories have been developed, such as bushings, ball (needle) bearings, etc. However, the Pei Lin referred to by the industry mostly refers to Ball (needle) Bearings, because they are used more frequently and widely.

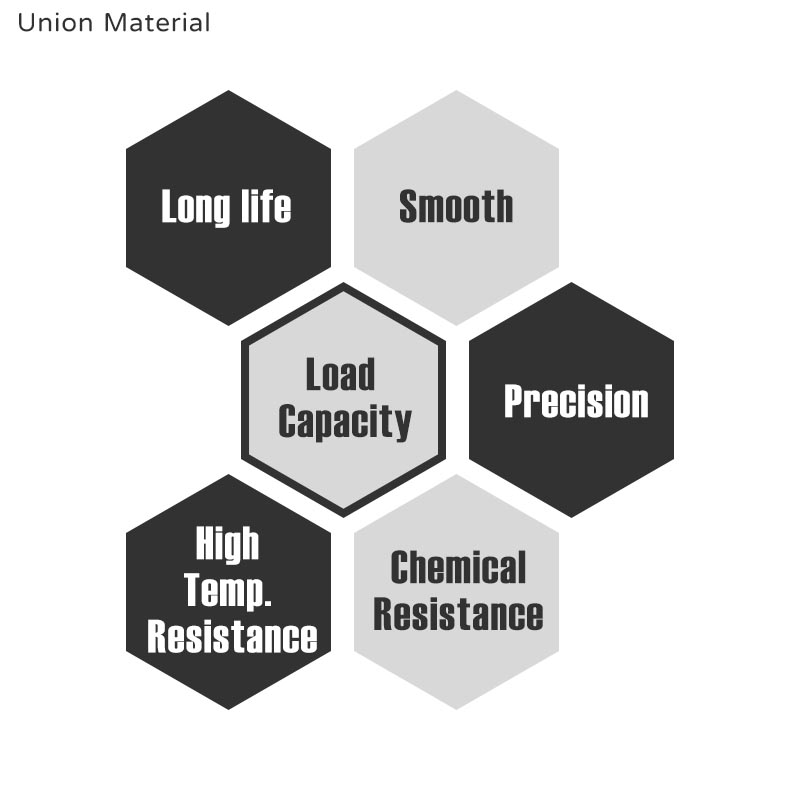
Requirements for bearing products
Common requirements for bearings are long life, smooth operation, large load capacity, high precision, low maintenance frequency, etc. Special environments may even require high temperature resistance, acid resistance, alkali resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and dirt resistance.
Introduction of new materials
As science and technology keep advancing, the materials and manufacturing methods for bearings are constantly evolving. For instance, plastic bearings are lightweight, capable of withstanding high temperatures and corrosive environments, and are increasingly popular in high-tech industries.
Bearings, seemingly insignificant small parts, play an irreplaceable role in our lives and industrial production. Through continuous technological innovation and material improvement, bearings will continue to play an important role in the stage of modern science and technology. The next time you enjoy the smooth operation of mechanical equipment, you might as well think about those unknown bearings that are silently supporting everything behind the scenes.



