Knowledge
What is bushing?

What is bushing
Bushing, Bushes
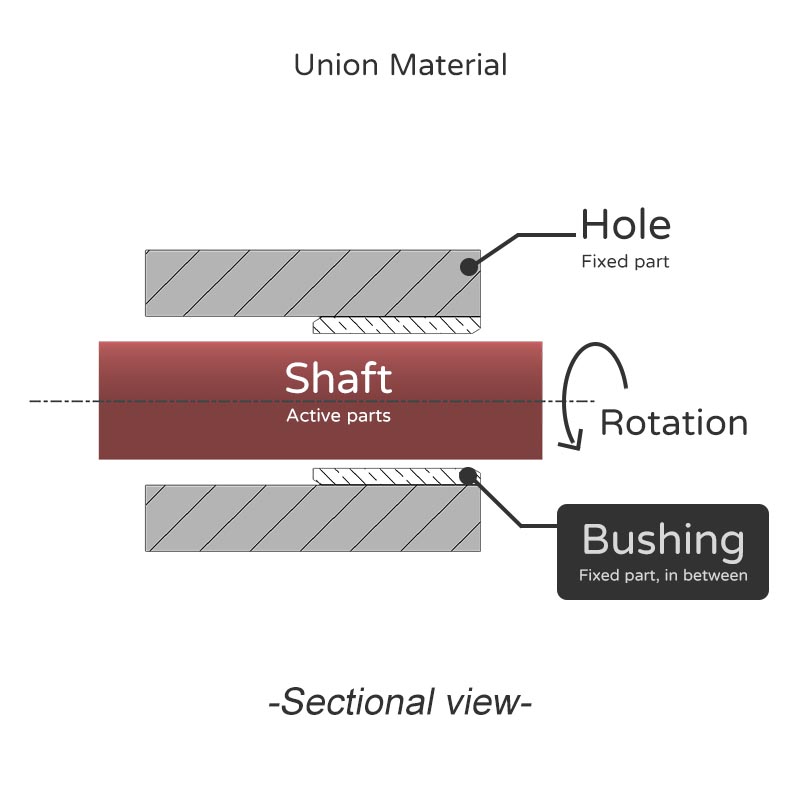
The shaft is one of the core parts of a machine and has the function of transmitting force by rotation.
The meaning of matching is to use an object between the hole and the shaft to act as a buffer and reduce friction and wear.
To sum up, the shaft liner is used to avoid wear and damage caused by direct surface contact between the shaft and the hole. The shaft liner can protect the shaft center and extend its service life.
Other Names
We have briefly sorted out the various terms used in the industry for bushings, and the different terms derived from them actually all refer to bushings, as follows:
- Plain bearing emphasizes appearance and function. It is flat and simple.
- Sleeve bearing emphasizes the appearance like a sleeve of clothing, is a hollow cylindrical object with thin walls.
- Linear bearing emphasizes the sliding straight line and linear movement.
- Journal bearing emphasizes the movement of rotation and twisting. You can imagine that a person’s neck can only rotate.
Type
A bushing is a simple sliding bearing, usually made of metal, plastic or other materials, used to provide friction between two contacting surfaces. There are many different types, suitable for a variety of different applications. The following are some common types of bushings
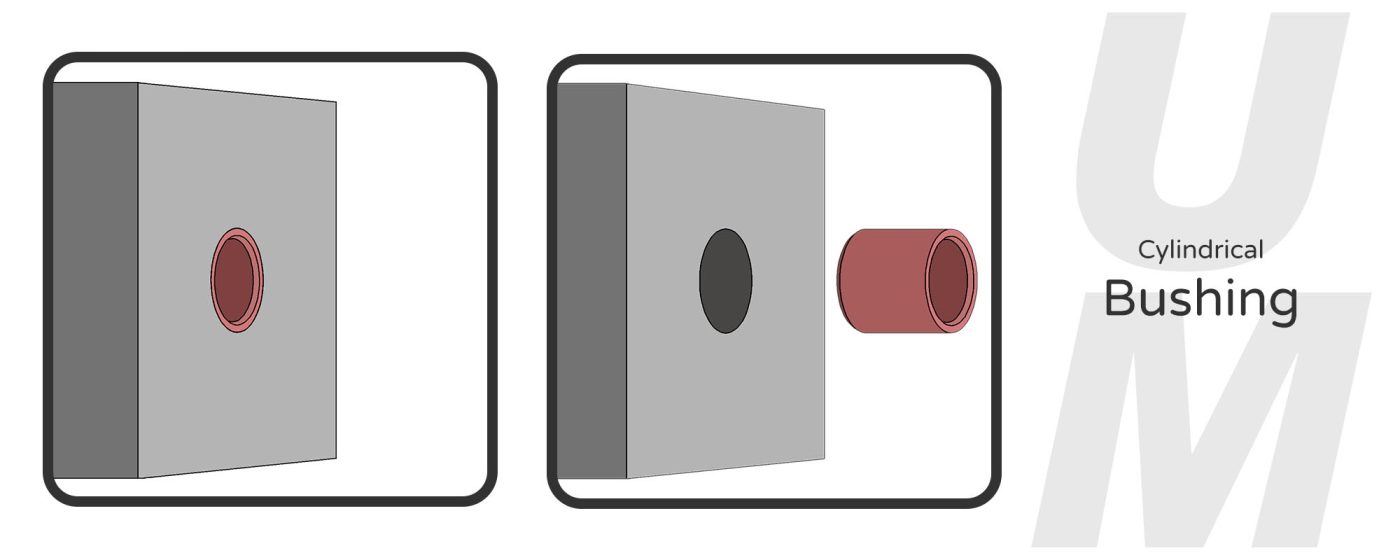
- Cylindrical bushings are cylindrical, hollow tubes that are installed in holes flush with the plane or buried inside. This is the most common bushing shape, often used in holes and on shafts, mainly for sliding and rotating movements, to reduce their friction and wear.
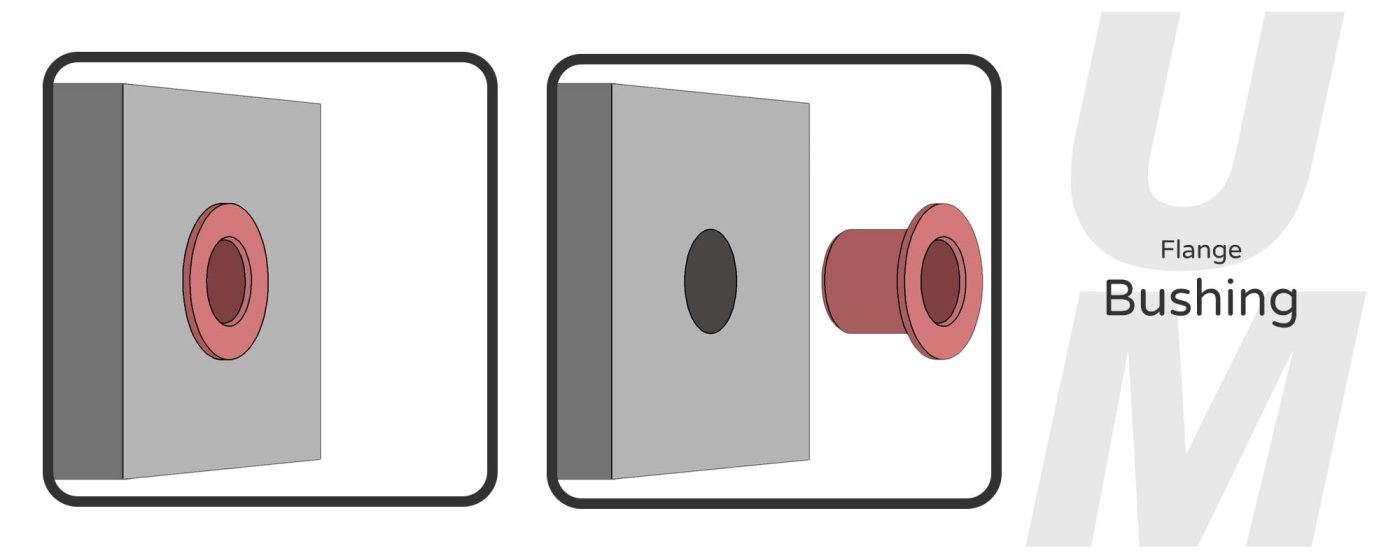
- Compared with the first one, the flange bushing has an additional disc at one end, which is called flange bushing for short. It can provide functions such as axial load, flat contact, and inhibit unidirectional displacement. It is used for more stable installation and positioning to prevent the bushing from moving during operation.
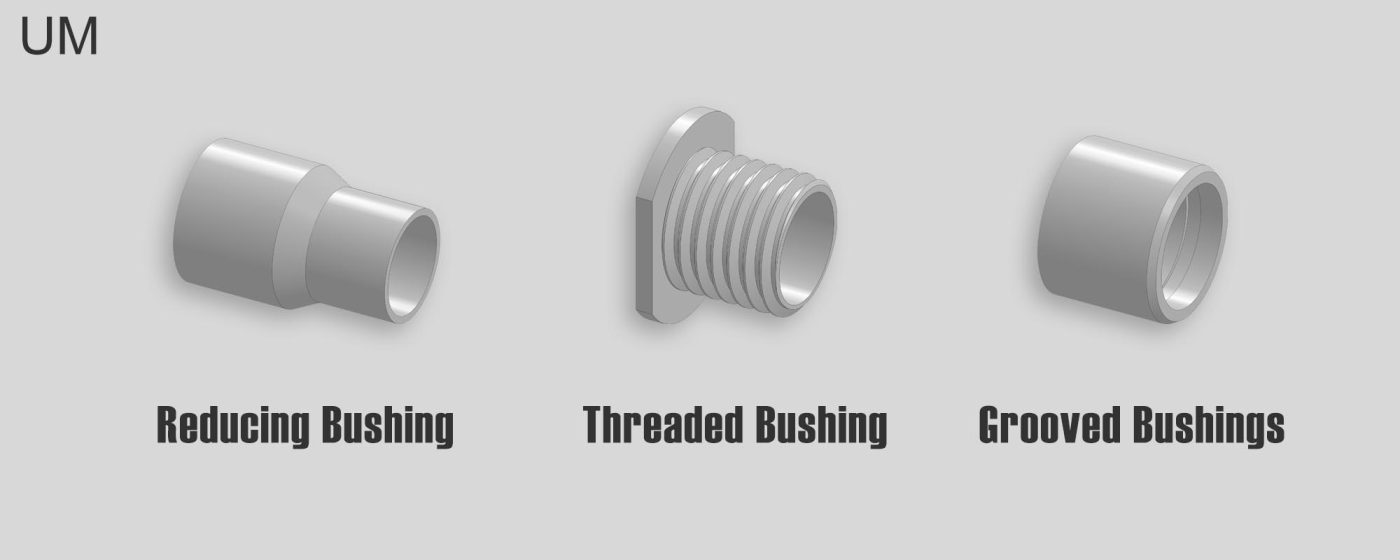
- Tapped bushing (threaded bushing), the bushing can be designed as a threaded type, which can be quickly placed in the hole and is firm.
- Reducing bushing, as a connector, connects pipes of different sizes.
- Grooved bushings have lubrication grooves set inside or outside the bushing to facilitate the distribution of lubricating oil, reduce friction and wear, and are suitable for mechanical equipment operating under high loads.
- Self-lubricating bushings, made of plastic, have the characteristics of self-lubrication, damping, shock absorption, buffering, energy transmission, etc.
Applications
They are widely used in a variety of applications due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Here are some common examples of bushing applications:
- Machine Tools: In a variety of industrial machine tools, bushings are used to support rotating components, provide smooth operation and reduce friction.
- Conveyor belt system: Bushings are used in conveyor belt rollers to help the rollers rotate smoothly and reduce energy consumption.
- Suspension System: Bushings are used in automotive suspension systems to provide shock absorption and a smoother ride.
- Doors and Windows: Bushings are used in tracks for sliding doors and windows to ensure smooth opening and closing action.
- Elevator Systems: Bushings are used in sliding and rotating components of elevators to provide smooth operation and reduce maintenance requirements.
- Tractors and harvesters: Bushings are used in rotating and sliding parts of agricultural machinery to enhance the durability and efficiency of the equipment.
Benefits of Bushings
Bushings have several obvious advantages in application
Self-lubricating property: The most special material among the bushing materials has self-lubricating properties, which reduces the need to add additional lubricating oil and reduce friction heat energy.
Low Cost: Compared with other types of bearings, bushings are generally lower in cost and are suitable for many applications with limited budgets.
Easy to maintain: The structure has fewer and simpler parts than ball bearings, making it easier to maintain the bushing.
Low Noise: The noise generated during operation is very small, which is very suitable for equipment and environments that require quiet operation.
Easy to install: The design structure is very simple, easy to manufacture and install.
Good adaptability: In high temperature, high pressure, dust or other harsh environments, the bushing can maintain better performance.
Light weight: The structure is reduced to several layers of parts, and the weight is greatly reduced, with only a single layer of material.
Large design space and flexibility: Compared with ball bearings, there is less space for inner rings, balls, retainers, etc., giving designers more space to use.
Reduce vibration: Bushings help reduce vibration during equipment operation, thereby improving the stability of the entire system

Disadvantages
- Limited load: Not suitable for high load and high speed operation, because sliding friction will generate more heat energy, that is, the limit PV value is used to evaluate whether the bushing can withstand the operating environment conditions.
- Regular Maintenance: Although some materials are self-lubricating, most still require regular lubrication and maintenance.
- Higher coefficient of friction: Greater friction than ball bearings and may require more energy to operate the equipment.
In general, bushings are suitable for low-speed, low-load applications. They have the advantages of high cost-effectiveness and simple structure, making them an ideal choice in many applications. However, in situations with high loads, high speeds and high precision, it may be necessary to consider using other types of bearings or solve the problem from a design perspective.
What is the difference with bearings
Bearing is a general term. Regardless of whether it is called a ball bearing, thrust bearing, oil-containing bearing, etc., or even a bushing, they can all be called bearings. It is a top-level general term, so when the object cannot be accurately named (or classified), it can be called a bearing.
Bushing is [one of all types of bearings]. It is the name of the second level, located below the bearing. Therefore, we can say that bushing is equivalent to bearing, but bearing is not equal to bushing. In other words, when we say bushing, we refer to this shape, and when we say bearing, we refer to one of many categories, and most of them may imply ball bearings.
The chart is merely the author’s opinion and understanding of the terms bearing and bushing, and may not be the standard answer, so it is for your reference only.

Generally speaking, bearings and bushings are both mechanical components used to support rotating shafts, but they have significant differences in design, application and characteristics.
Bearings
- It is composed of several parts, including rolling elements and retainers, such as balls, rollers, etc.
- Complex design and high cost
- Suitable for applications that require high loads and high speeds
- Complex structure, high manufacturing and maintenance costs
- Rolling elements significantly reduce friction and improve efficiency
- Suitable for a variety of motion types, including rotational, axial and radial motion
- It is composed of several parts and takes up a lot of space.
- Heavy weight
- Suitable for high precision applications
- Well designed, Long service life
Bushings
- Relies on sliding contact to support the shaft, no rolling elements
- Simple design and low cost
- Suitable for low speed and light load applications
- Lower manufacturing and maintenance costs
- Sliding friction is greater than rolling friction and is less efficient
- A variety of materials are available to adapt to different environments
- Fewer parts and less space
- Light weight
- Low operating noise, suitable for environments that require quietness
- It is easy to wear out after long-term use and still needs to be replaced regularly
- Certain materials have self-lubricating properties, reducing maintenance requirements